YRP UNL has conducted research on realizing how to retrieve information about objects, and check or trace such objects by assigning ID numbers to everything including physical or abstract objects, that are countable and namable, anytime, anywhere.
The ID is a unique number so each item can be identified uniquely. It is called ‘ucode’. YRP UNL proposed the concept and the application framework based on the code as “uID Architecture”. The uID Architecture is Open Architecture, in the sense that the necessary specification and API to access servers are published.
uID Architecture 2.0 (u2) is the advanced form of uID Architecture employing new ucode specification (ucode2.0), enables integrated cross-domain queries for large amount of data in various formats collected in computer networks, and expands the targets of its application. Also u2 promotes mashup with various other services, data linkage across organizations and easy use from mobile apps.
The case studies can be found in “Applied Research”.

About ucode2.0
YRP UNL has conducted research and development of the fundamental technology of ucode2.0 to advance uID technology. ucode refers to the identification system, and to individual number, number assigned to individual objects. It is defined as 128 bits long identification number and is the basis of the International Telecommunication Union Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T) recommendation. Currently, platforms for location information system, open data application, and a discovery service in the IoT environment etc. have been built.
In order to advance this ucode further and to realize the IoT, ucode2.0 that can offer more advanced application framework has been proposed. It is used as the infrastructure for the various platforms, such as IoT-Aggregator, OpaaS.io (a PDS) etc., that YRP UNL has built and operated in collaboration with other parties to realize Aggregate Computing.
ucode2.0 has the following characteristics in contrast with the legacy ucode technology (ucode1.0). Previously, the basic width of ID area was 96 bits but it has been widened to 124 bits so that more ucodes can be issued. uID (ucode) is assigned to information that manages ucode system itself, and u2 avoids including meaning in the ID area.
Format of ucode2.0
| 4bits | 124bits |
| Version | Identification Code |
- Version number (version) is defined as 0x
- It is customary to write a ucode in 32 hexadecimal digits.
ucode2.0 has more possibilities of application in real world.
① Authority to issue ucode and ② ownership of ucode can be transferred to a third party.
E.g. An owner of ucodes can transfer :
① the authority to issue ucodes of a company’s brand to a factory
② a shop’s ownership of a ucode of an item to a purchaser when the item is sold at the shop
Attribute information is classified by industrial segments or application fields, and managed on the ucode2.0 platform.
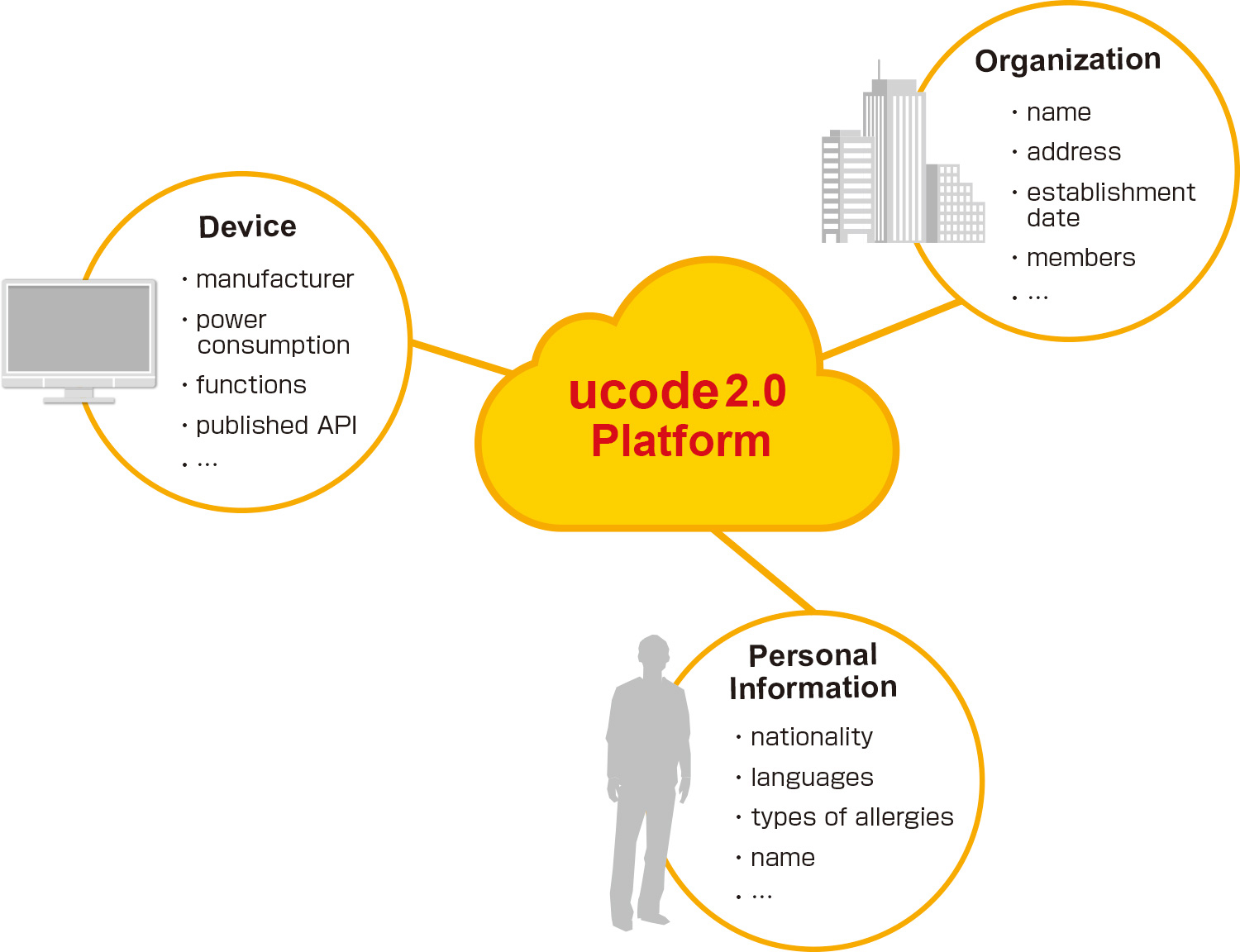
Expanding service offerings
Provide ucode issue API as Web API. This was not previously offered to the public.
⇒ ucode platform can now be used as PaaS. This saves time and manpower for the application development.
International Standardization of uID Technologies
YRP UNL has created standardization with ITU and the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF).
ITU
The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) is a specialized agency of United Nations. The organization defines the standards to enable global wireless communication and telecommunication.
ITU-T is the Telecommunication Standardization Sector of the ITU, which establishes recommendation in the telecommunication field (“standardization” is called “recommendation” in ITU).
YRP UNL promoted ucode, for uID architecture that is the IoT fundamental technology, to be recommended and it was standardized as ITU recommendation. The standardizations that YRP UNL promoted taking initiative and recommended by the ITU-T are as follows:
- Y.4551/F.771 :F.771: Service description and requirements for multimedia information access triggered by tag-based identification
- Y.4405/H.621:H.621: Architecture of a system for multimedia information access triggered by tag-based identification
- H.642.1:H.642.1: Multimedia information access triggered by tag-based identification – Identification scheme
IETF
The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) establishes standards of technologies applied in the Internet. The fundamental technologies such as TCP/IP etc. are all standardized by the IETF.
There are various ways to store ID by software into devices that can be connected to the Internet.
One of them is to convert ID into byte sequence then store it. This is called Uniform Resource Name (URN) form.
Next standard is the document that determines URN format applied to store ucode.
A device or software connected to the Internet enables reading and writing ucode in URN format anywhere in the world beyond organizations and nations.
RFC6588: A URN Namespace for ucode
In this way, YRP UNL opens the information of the necessary technologies for the IoT, and publishes as standardized.
